Understanding Peptic Ulcers: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Verified By Admin | 26-Nov-2023
Peptic ulcers are a common and often misunderstood condition affecting the gastrointestinal tract. These painful sores can develop in the lining of the stomach, small intestine, or esophagus, and they can lead to various symptoms and complications if left untreated. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of peptic ulcers, exploring their types, causes, symptoms, and the latest advancements in their management and treatment. We’ll also introduce you to the expertise of top gastroenterologists, including those at Kailash Hospital in Noida, who specialize in providing exceptional care for gastrointestinal conditions.
Types of Peptic Ulcers
Peptic ulcers are typically classified based on their location within the digestive tract:
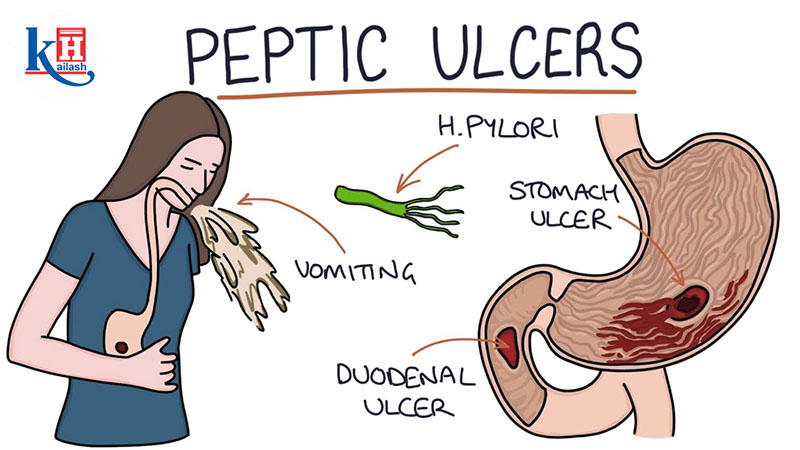
- Gastric Ulcers: These ulcers develop in the lining of the stomach and are known as gastric ulcers. They are the most common type of peptic ulcer.
- Duodenal Ulcers: Duodenal ulcers form in the first part of the small intestine, known as the duodenum. They are the second most prevalent type of peptic ulcer.
- Esophageal Ulcers: These ulcers occur in the lower part of the esophagus and are less common than gastric and duodenal ulcers.
Causes of Peptic Ulcers
For many years, it was believed that peptic ulcers were primarily caused by stress and spicy foods. However, research has revealed that the majority of peptic ulcers are actually caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) or the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Here’s an overview of the common causes:
- pylori Infection: H. pylori is a bacteria that can weaken the protective mucous lining of the stomach and small intestine, making them more susceptible to damage from stomach acid.
- NSAIDs: Regular use of NSAIDs like aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen can irritate the stomach lining and increase the risk of peptic ulcers.
- Smoking: Smoking cigarettes or using other tobacco products can increase the risk of peptic ulcers and slow down the healing process.
- Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can irritate the stomach lining and exacerbate peptic ulcer symptoms.
- Stress: While stress can exacerbate existing ulcers, it is not considered a primary cause.
Symptoms of Peptic Ulcers
The symptoms of peptic ulcers can vary in severity and may come and go over time. Common symptoms include:
- Burning Pain: A burning or gnawing pain in the abdomen, typically between the breastbone and the navel, is a hallmark symptom of peptic ulcers. The pain may improve after eating or taking antacids but can return between meals or at night.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Some individuals with peptic ulcers may experience nausea and vomiting, which can worsen after eating.
- Bloating: Abdominal bloating and a feeling of fullness, even with a small meal, can be indicative of an ulcer.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: In some cases, peptic ulcers can lead to unexplained weight loss due to reduced appetite and discomfort after eating.
- Dark or Bloody Stools: Peptic ulcers can cause bleeding in the stomach or small intestine, leading to dark, tarry stools or stools that appear bloody.
- Heartburn: Some people with peptic ulcers may experience heartburn, especially if stomach acid flows back into the esophagus.
Treatment Options for Peptic Ulcers
The management and treatment of peptic ulcers depend on their cause and severity. Here are common approaches:
- Antibiotics: If H. pylori infection is the cause, a course of antibiotics is prescribed to eradicate the bacteria. This treatment may be combined with medications to reduce stomach acid production.
- Acid-Reducing Medications: Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and histamine H2-receptor antagonists (H2 blockers) are commonly prescribed to reduce stomach acid production, allowing ulcers to heal.
- Cytoprotective Agents: Medications like sucralfate can help protect the lining of the stomach and promote healing.
- Avoiding Irritants: Patients are advised to avoid NSAIDs, alcohol, and smoking to prevent further irritation of the ulcer.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Dietary and lifestyle changes, such as eating smaller, more frequent meals and managing stress, can help manage symptoms and promote healing.
- Endoscopy: In severe cases or if there is bleeding, an endoscopy may be performed to directly visualize the ulcer and stop the bleeding.
- Surgery: Surgical intervention may be necessary in rare cases when complications like perforation or obstruction occur, or if ulcers do not respond to medical treatment.
Kailash Hospital, Noida: One-stop-solution for Gastrointestinal Care
Kailash Hospital in Noida is a renowned healthcare facility equipped with a team of top gastroenterologists and state-of-the-art facilities to diagnose and treat peptic ulcers and a wide range of gastrointestinal conditions. Our patient-centric approach ensures that the patients receive personalized care and the latest advancements in the field of gastroenterology.
If you suspect you have a peptic ulcer or are experiencing related symptoms, seek early diagnostics and care from a gastroenterologist at Kailash Hospital, Noida.


 +91-9711918451
+91-9711918451
 international.marketing@kailashhealthcare.com
international.marketing@kailashhealthcare.com







