List of Top Angioplasty doctors near by
Talk to our doctors
Angioplasty
The human body is an intricate network, with our arteries serving as essential routes that transport oxygen-rich blood throughout our system. When these pathways become narrowed or blocked by plaque buildup (atherosclerosis), blood flow can become restricted, leading to a variety of health concerns. Angioplasty offers a minimally invasive procedure to restore blood flow and improve cardiovascular health.
Understanding Angioplasty
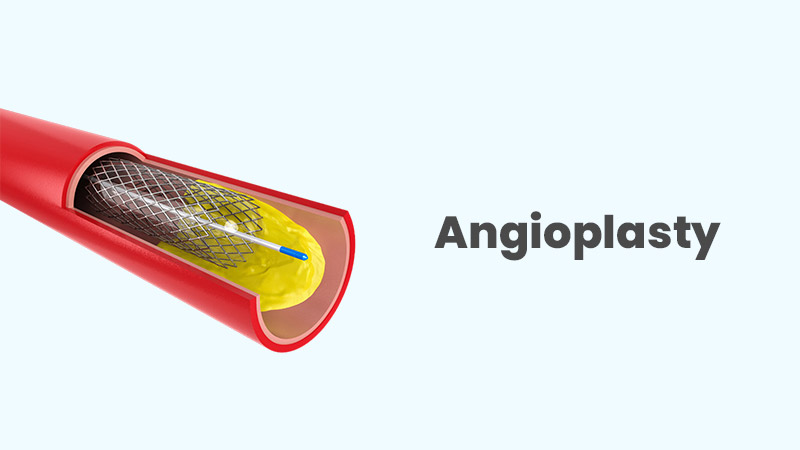
Angioplasty, also known as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), is a procedure that widens narrowed or blocked arteries in the heart. This is typically achieved by inserting a thin, flexible tube called a catheter into a blood vessel in the groin, arm, or wrist. Using X-ray imaging, the catheter is then guided to the blocked artery. Once in place, a tiny balloon at the tip of the catheter is inflated, pushing against the plaque buildup and widening the artery to improve blood flow.
Who Needs Angioplasty?
Angioplasty is often considered for individuals experiencing symptoms of coronary artery disease (CAD), such as chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, or fatigue. These symptoms arise due to the restricted blood flow to the heart muscle. Here are some common scenarios where angioplasty might be recommended:
- Angina: Chest pain that occurs with exertion and improves with rest.
- Atherosclerosis: Angioplasty is recommended if you have blockages in your coronary arteries.
- Heart attack: Angioplasty is performed during a heart attack to treat a blocked artery and minimize heart damage.
The Angioplasty Procedure
Angioplasty is typically performed in a specialized cardiac catheterization laboratory within a hospital setting. Here's a breakdown of the process:
- Pre-operative Evaluation: A thorough evaluation by a qualified angioplasty doctor in Noida is crucial. This involves discussing your medical history, symptoms, and medications. The doctor will perform a physical examination and order tests like electrocardiograms (ECGs) and coronary angiograms (X-ray imaging of the heart's arteries) to assess the extent of blockage.
- Preparation: On the day of the procedure, you will likely be instructed to avoid eating or drinking for several hours beforehand. You might be prescribed medications to help you relax during the procedure.
- The Angioplasty Process: The doctor inserts a catheter into a blood vessel in your groin, arm, or wrist. Using X-ray guidance, the catheter is navigated to the blocked artery. A small balloon on the catheter tip is then inflated to widen the narrowed artery. In some cases, a stent, a tiny mesh tube, might be placed within the artery to help it remain open. The entire procedure usually lasts between one and two hours.
- Recovery: Following the procedure, you will be monitored for a few hours to ensure proper blood flow and function of the treated artery. Most patients can be discharged within one to two days.
Lifestyle after Angioplasty
While angioplasty successfully opens blocked arteries, lifestyle modifications are crucial for long-term success. Here's what you can expect after angioplasty recovery:
- Medication Management: Your doctor might prescribe medications like aspirin, cholesterol-lowering medications, and blood thinners to prevent future blockages.
- Cardiac Rehabilitation: A personalized rehabilitation program can help you strengthen your heart and improve your overall fitness.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, and managing stress are essential for preventing future heart problems.
Angioplasty offers a valuable tool for restoring blood flow and improving heart health. By working closely with your doctor, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and adhering to prescribed medications, you can significantly reduce your risk of future heart complications and live a more fulfilling life.
FAQ'S
Angioplasty restores blood flow by opening narrowed or blocked arteries, improving heart function.
Angioplasty is less invasive, using a catheter to clear blockages, while bypass surgery involves creating new routes for blood flow.
Most patients stay 1-2 days, with some discharged the same day if no complications arise.
Patients are advised to eat a heart-healthy diet, avoiding fatty and processed foods to maintain artery health.
The procedure typically lasts 30 minutes to 2 hours, depending on the complexity of the blockage.
While angioplasty improves blood flow, lifestyle changes and medications are necessary to prevent new blockages.
The procedure itself is painless due to anesthesia, though some mild discomfort may occur during catheter insertion.
Related Blogs
Patient Reviews & FeedBack
© 2025 Kailash Healthcare Ltd. All Rights Reserved





 D. S. GambhirKailash Hospital, Noida.jpg)





.jpg.jpg)










